Reports of issues associated with the use of Cathejell (lignocaine 2% gel)
Lignocaine Gel 2% w/w (Cathejell, Pharmaforte Singapore Pte Ltd) is a local anaesthetic in sterile gel form, and is used as a lubricant for catheters, endoscopes or other medical instruments. When applied to mucous membranes, its local anaesthetic and lubricant effects help to alleviate pain during these interventions. Cathejell is currently the only registered sterile lignocaine product in Singapore available in a syringe formulation. Its accordion syringe design with a break-off tip (Figure 1) differs from the design of a traditional syringe. Since late 2022, Cathejell has become more widely used in thepublic and private healthcare institutions and clinics locally. Cathejell is also marketed in the European Union (EU) and other countries such as Canada and Australia.

Figure 1. Cathejell’s accordion syringe and break-off tip design.
Issues and adverse events with Cathejell
Following the initial feedback received from healthcare professionals in December 2022 which described difficulties with Cathejell when used in procedures such as indwelling catheter (IDC) insertion or cystoscopy, HSA solicited information from other healthcare institutions using Cathejell to better understand the extent of the issue. Not all healthcare institutions experienced similar issues; for those that gave feedback, most of the issues appeared to be related to the accordion syringe design. These include difficulty in controlling the amount of gel dispensed due to the incremental pressure required during administration, making it hard to expel the entire contents of the syringe. This resulted in multiple syringes being used, gel leakage and wastage. Another feedback was that the vacuum created upon the release of the accordion syringe caused a suction effect. This suction effect may cause pain to the patient, or abrasion to the urethral mucosa which can lead to bleeding at the administration site. There was also feedback associated with the length of the tip, as well as the tip being too sharp or having a rough edge.
Three AE cases of administration site bleeding with Cathejell were reported to HSA by two clinicians. In one case, penile tip bleeding occurred following Cathejell administration prior to cystoscope insertion, which the user attributed to an inability to control the amount of gel dispensed due to the syringe design. In the second case, bleeding occurred following Cathejell administration in a patient with benign prostate hyperplasia, and the user attributed it to a product design issue. In the third case, bleeding from the penile urethra occurred when Cathejell was administered for urine catheter insertion.
HSA’s assessment and follow-up actions
Taking into consideration the three AE cases as well as the information gathered, the cause of the issues could be multifactorial, such as users being unfamiliar with Cathejell’s specific administration techniques or Cathejell’s inherent product design. Since receiving the feedback, the product registrant has strengthened its efforts in reaching out to end-users to conduct training sessions to reinforce the administration techniques of Cathejell. HSA has worked with the product registrant to update and highlight the administration method on the product’s packaging such as the package insert, outer carton (Figure 2) and inner label of individual blisters (Figure 3). HSA has also required the product registrant to strengthen its communication to new users on the administration techniques of Cathejell. These measures aim to increase awareness on the administration techniques and to mitigate potential risks of AEs. HSA will continue to monitor the situation and determine if further measures are necessary. Healthcare professionals who encounter issues with Cathejell are encouraged to provide feedback and report any AEs to HSA. Users may also reach out to the product registrant at pharmacist@pharmaforte.com.sg or +65 64528488 for any queries regarding Cathejell or requests for product training and demonstration.
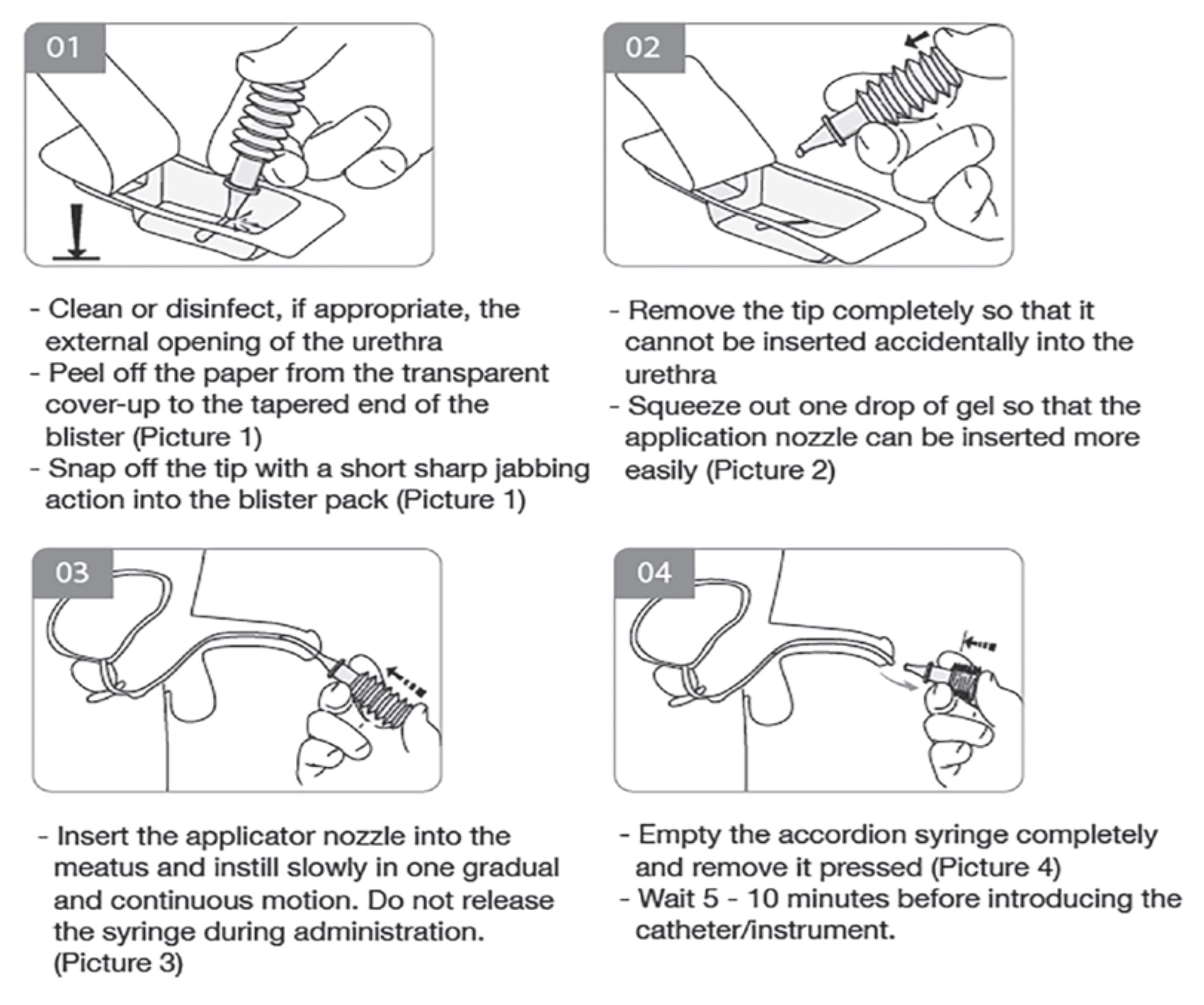
Figure 2. Cathejell’s administration method on the outer carton

Figure 3. Cathejell’s administration method on the inner label of individual blisters
Healthcare professional, Industry member, Therapeutic Products
Published:
Safety Alerts